Interact workflow for implementing the marketing plan
When you configure Interact, you use a workflow to outline the process from an idea to deployment in detail. Configuring Interact is a multi-step, multi-person, iterative process. The process from an idea to deployment involves: design, configuration, testing, review, and deployment.
Workflow process
- Design the interaction. During the design step, the team identifies the interaction points, zones, events, and categories in the interactive channel. The Interact administrator uses the names of the interaction points and events and configures the touchpoint with the Interact API. The Interact user uses the user interface to enter the components into the system.
- Configure the interaction. The design is configured in Campaign and Interact. The using interactive flowcharts in Campaign, the Interact API, and the Interact user interface. The Campaign and Interact users are involved in the configuration as sell as the Interact administrator, who works with the Interact API.
- Test the interaction. The Interact user and administrator create the interaction components in Interact. Then, the Interact administrator deploys them to a staging server for testing.
- Review the interaction. After the interaction is tested, review it again before deployment.
- Deploy the interaction. The administrator deploys the interaction to the production server.
Design the interaction
During the design phase, you brainstorm about what kinds of interactive marketing strategies you would like to use. When you have a strategy for how you want the visitor to interact with your touchpoint, you need to determine how to implement that strategy with Interact.
- Manages the touchpoint with the Interact API
- Works with the Interact user interface
- Designs the marketing plan
Configure the interaction
During the configuration phase, the touchpoint administrator and an Interact user implement the design. The Interact user defines offer-to-segment assignments and configures the interactive channel with the user interface in the design environment. The Interact administrator configures the Interact API to make the touchpoint work with the runtime server. The data administrator configures and creates the data tables that are required for both testing and production.
Test the interaction
After the interaction is configured in the Interact design environment, you mark the various components for deployment to staging runtime environments. The Interact administrator deploys the configuration to the staging servers and the testing can begin.
- Configured interaction is working as designed
- Performance of the runtime environment is within tolerable limits for response time and throughput
The designers might need to change the design and more testing might need to be done. After everyone is pleased by the results, the manager can mark the configuration for deployment to production servers.
Review the interaction
After testing, the touchpoint manager can review all the results as well to ensure that the configuration will have no adverse effects on the customer-facing system.
Deploy the interaction
After the configuration has approval from all parties, it can be deployed to production runtime servers.
Design workflow diagram
This diagram shows a sample design workflow.
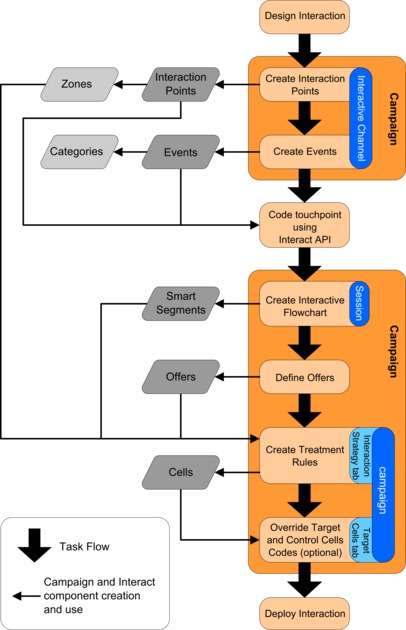
While this diagram shows a linear progression, in practice, many people are working on different components at the same time. It is also an iterative process. For example, to use Interact API to configure the touchpoint to work with Interact, the administrator must reference events that are created in the interactive channel. As the Interact administrator configures the touchpoint in the runtime environment, the administrator might realize that more events are needed. After they are approved by the design team, the Interact user creates these events in the design environment.
