Configuring a Domino LDAP server for Nomad
Before you begin
Note: We recommend using port
636 for better security.
About this task
Procedure
-
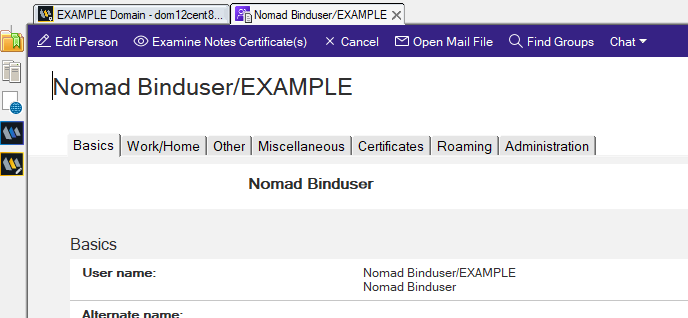
Create a Bind User.
Nomad server should use a dedicated system user ("bind user") to search the Domino LDAP directory for the necessary information. This "bind user" can be any Domino user with read-access to the Domino server's names.nsf and a set Internet-Password. The following is an example of a bind user:
-
Set default server settings.
For Domino LDAP to function properly, you must create a "Default Server Configuration" document in the Domino Directory. The following is an example of a Configuration Settings document:
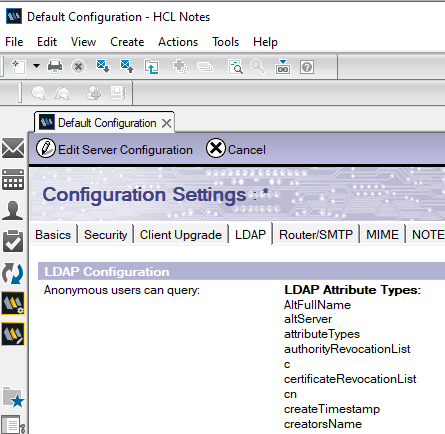 For more information, see Creating a Configuration Settings document in the HCL Domino documentation.
For more information, see Creating a Configuration Settings document in the HCL Domino documentation. -
Ensure that the LDAP service has access to search the following required
attributes:
dominoPersonobjectclass attributes:mailDomain,MailServerdominoServerobject class attribute:SMTPFullHostDomain
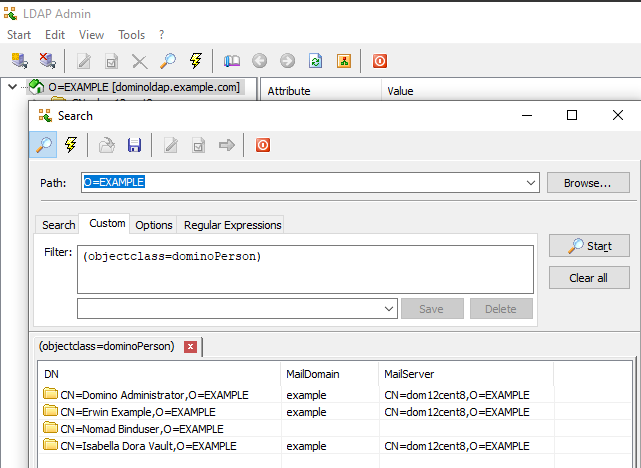
SafeLinx uses the Domino LDAP service to query the Domino directory for attributes about users and Domino servers.Verifying from a Linux command line:Domino person attributesIssue the following command to get the
mailDomainandMailServerattributes for all users in the Domino Directory via LDAP.-hspecifies the FQDN of the Domino LDAP server-Dspecifes the distinguished name (DN) of the bind-user you will use for the Nomad server bind-user-bspecifes the "base distinguished name (DN)" where the LDAP search will start searching. Verify that your chosen "base DN" covers BOTHdominoPersonANDdominoServerobjects.
ldapsearch -LLL -p 389 -h dominoldap.example.com -D "CN=Nomad Binduser,O=EXAMPLE" -W -b "O=EXAMPLE" "(objectclass=dominoPerson)" mailDomain MailServerWhich returns something similar to:dn: CN=Domino Administrator,O=EXAMPLE mailDomain: example MailServer: CN=dom12cent8,O=EXAMPLE dn: CN=Erwin Example,O=EXAMPLE mailDomain: example MailServer: CN=dom12cent8,O=EXAMPLE dn: CN=Nomad Binduser,O=EXAMPLE dn: CN=Isabella Dora Vault,O=EXAMPLE mailDomain: example MailServer: CN=dom12cent8,O=EXAMPLEDomino server attributesIssue the following command to get the
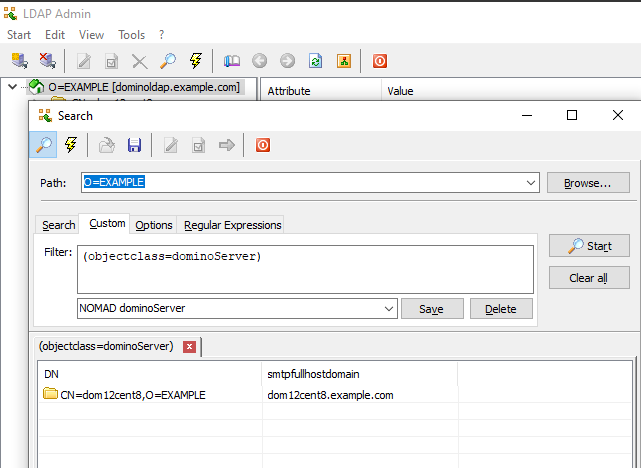
SMTPFullHostDomainattribute for all servers in the Domino Directory via LDAP.-hspecifies the FQDN of the Domino LDAP server-Dspecifes the distinguished name (DN) of the bind-user you will use for the Nomad server bind-user-bspecifes the "base distinguished name (DN)" where the LDAP search will start searching. Verify that your chosen "base DN" covers BOTHdominoPersonANDdominoServerobjects.
ldapsearch -LLL -p 389 -h dominoldap.example.com -D "CN=Nomad Binduser,O=EXAMPLE" -W -b "O=EXAMPLE" "(objectclass=dominoServer)" SMTPFullHostDomainWhich returns something similar to:dn: CN=dom12cent8,O=EXAMPLE SMTPFullHostDomain: dom12cent8.example.comVerifying on Windows:In order to verify LDAP access via Microsoft Windows, please install a Windows GUI-based LDAP browser/client of your choice.
- When verifying the dominoPerson attributes, please make sure to use the bind-user and "base distinguished name (DN)" that you will also use when configuring the Nomad server.
- Verify that your chosen "base DN" covers BOTH
dominoPersonANDdominoServerobjects.
Domino person attributes