Tunneling through the firewall when SSL is enabled
Configure an IBM® Sametime® server to allow clients to tunnel through a firewall when SSL is enabled.
Before you begin
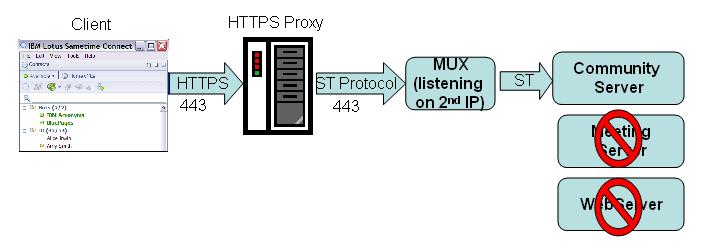
Sametime Connect Client communicate with the Sametime server by directing messages to the HTTP server, which listens on port 80. When SSL is enabled, port 443 is normally used for sending encrypted messages; however, the Domino® server (which hosts Sametime) is already listening on port 443 for encrypted Web-based communications. If Sametime Connect Clients also send messages to the HTTP server on port 443, a conflict arises.
You can work around this conflict by configuring clients to access the Sametime server by tunneling to its Community Services multiplexer with an HTTPS proxy. In this type of configuration, both the Sametime Community Server and the Domino server listen for Connections on port 443 - but they use different addresses to avoid conflicts. You set up this type of connection by assigning an additional IP address to the Sametime server, and then configuring both the Community Services multiplexer and your clients to use that address when communicating on port 443.
The following picture shows an example of this type of connection:
About this task
If you want to allow clients to tunnel to the Community Services multiplexer on port 443 when SSL is enabled, complete the following tasks: