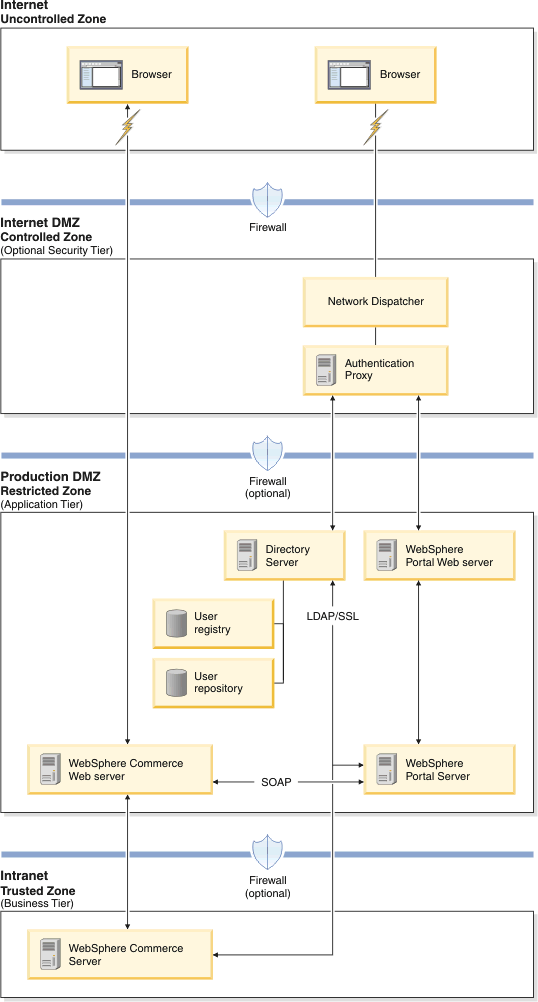
WebSphere Commerce Portal Integration site architecture
The WebSphere Commerce Portal Integration sample site architecture includes relationships between the Internet, Internet DMZ, Production DMZ, and intranet.
The following diagram depicts a sample architecture with WebSphere Portal and WebSphere Commerce deployed in a multitier DMZ configuration with high availability. This sample configuration can be used for an Internet or extranet WebSphere Portal solution. In this configuration, an optional authentication proxy, such as Security Access Management Family WebSEAL, can be used to shield the web server from unauthorized requests for external facing users. Use this approach when the web server or the application server contains sensitive data, such as order-related information, where direct access to it is not desirable. If WebSphere Application Server is used for authentication, which is the default WebSphere Portal configuration, it uses a directory server, such as an LDAP server to verify credentials:
The security model for WebSphere Commerce Portal Integration assumes the network connection between the WebSphere Portal tier and the backend WebSphere Commerce tier are either behind a firewall or secured. It is up to the WebSphere Portal administrator to decide which networking model to employ. The decision should be weighted between the benefit and the cost of using secured connections.
Configuring WebSphere Portal to use SSL adds security so that all traffic between the WebSphere Portal Server and the back-end WebSphere Commerce services is encrypted. This added security prevents any eavesdropping on the information that is exchanged over the network. However, depending on the amount and nature of the information that is being transferred, the cost of encryption can sometimes have a sufficient impact on the overall application performance.
There are primarily two kinds of users of this sample configuration: shoppers and business users. The access route of online shoppers is different from how internal business users access the WebSphere Commerce system. Internal business users typically have special credentials to access the trusted backend network. Then, users can use native WebSphere Commerce user interfaces to configure the online store and product information. Shoppers, however, require a higher level of defense security when they access the site content. To prevent unauthorized requests, and other potential security exposures.
The following diagram represents the recommended sample deployment and network configuration for WebSphere Commerce and WebSphere Portal integration:
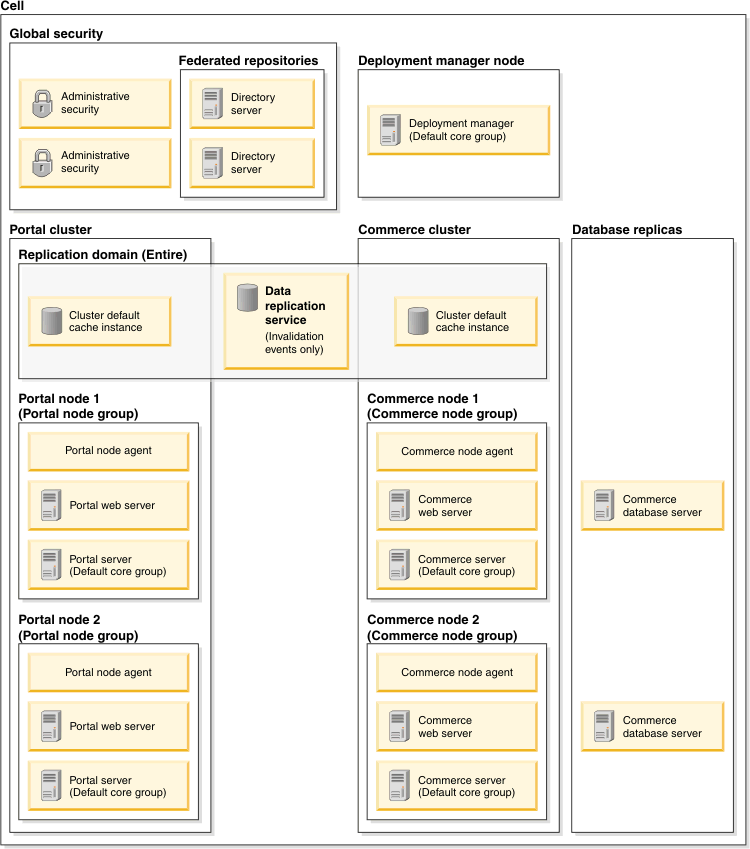
In this sample, the single cell network configuration is necessary for implementing the cache invalidation function between WebSphere Commerce and WebSphere Portal. It creates a secured domain as a WebSphere Application Server cell with two separate clusters, each consisting of a set of WebSphere Commerce nodes and WebSphere Portal nodes. A replication service is used to broadcast only cache invalidation events between the two clusters, which are part of the same replication domain and core group.
- All WebSphere Commerce nodes must belong to the same node group.
- All WebSphere Portal nodes must belong to the same node group. This node group can be different from the WebSphere Commerce node group.
- All WebSphere Commerce nodes must be assigned to the same cluster. This cluster must not contain any WebSphere Portal nodes.
- All WebSphere Portal nodes must be assigned to the same cluster. This cluster must not contain any WebSphere Commerce nodes.
- All nodes, both WebSphere Commerce and WebSphere Portal, must be part of the same core group.
- Both the WebSphere Commerce cluster and WebSphere Portal cluster must be deployed to the same cell.
- For each WebSphere Portal application server, enable the web container servlet cache, with the Portlet container portlet cache disabled.
- All application servers, both WebSphere Commerce and WebSphere Portal, must have DynaCache replication enabled against the same replication domain. The application servers must have the replication enabled with the Not Shared replication type to broadcast invalidation events only.
- Each cluster must have a cache instance that can be used for cache replication.
- Enable cell-level global security with federated LDAP repositories in order for LTPA single sign-on to work.
- Web servers that can be used with cluster members are recommended, but not required.
Uncontrolled zone
The uncontrolled zone contains:
- Users who attempt to access the WebSphere Portal application or the WebSphere Commerce application directly.
Controlled zone
The controlled zone contains:
- A firewall.
- An authentication proxy such as Security Access Management Family. This authentication proxy is placed behind a firewall and manages the authentication process.
Restricted zone
The restricted zone contains:
- A firewall.
- A web server that serves the WebSphere Portal application.
- A WebSphere Portal machine that contains the WebSphere Commerce Portlets. The portlets can access the WebSphere Commerce application over a secure SSL connection and through an extra firewall.
- An LDAP server such as Tivoli Directory Server, provides access to the user registry and user repository. This repository can be accessed by the WebSphere Portal machine over a secure SSL connection.
Trusted zone
The trusted zone contains:
- A firewall.
- An optional web server that serves the WebSphere Commerce application directly.
- The WebSphere Commerce application. This application can communicate with the WebSphere Commerce Portlets over a secure HTTPS connection.
- The WebSphere Commerce application can communicate with the LDAP server over an SSL connection and through a firewall.
For more information about using SSL in WebSphere Portal, see Setting up SSL.