IBM Virtual processor core (VPC)
![]() Available from 9.2.11. IBM virtual processor core (VPC) is a
unit of measurement that is used to determine the licensing cost of BigFix products. It is based
on the number of virtual cores (vCPUs) that are available to the product. A vCPU is a virtual core
that is assigned to a virtual machine or a physical processor core if the server is not
partitioned for virtual machines.
Available from 9.2.11. IBM virtual processor core (VPC) is a
unit of measurement that is used to determine the licensing cost of BigFix products. It is based
on the number of virtual cores (vCPUs) that are available to the product. A vCPU is a virtual core
that is assigned to a virtual machine or a physical processor core if the server is not
partitioned for virtual machines.
Scenarios
The following scenarios describe how the number of vCPUs is counted under different circumstances. The calculations are based on sample values and should be treated as examples.
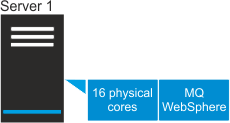
- Scenario 1: VPC on a physical server
- IBM MQ software is installed on a server that has two processors. Each processor has 8 physical
cores which gives 16 cores in total. The number of vCPUs to license is 16.
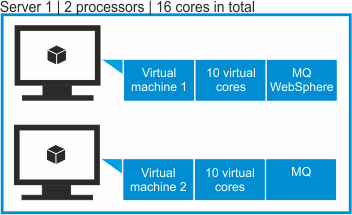
- Scenario 2: VPC on two virtual machines
-
Two VMs are deployed on a server that has two processors. Each processor has 8 physical cores which gives 16 cores in total. Each VM is assigned 10 vCPUs.
WebSphere software is installed only on the first VM and has access to 10 vCPUs. The number of vCPUs to license is 10. IBM MQ software is installed on both VMs and thus has access to 20 vCPUs. Because the number of physical cores is lower than the number of vCPUs that are assigned to the VMs, the number of vCPUs to license is capped to 16.
- Scenario 3: VPC in a virtual environment where the VM manager is not defined
-
Important: This scenario is not supported. It is provided to explain the consequences of not defining the VM manager that controls resources that are available to virtual machines. VM managers must be defined to properly report VPC consumption.
Two VMs are deployed on a server that has two processors. Each processor has 8 cores which gives 16 physical cores in total. The first VM is assigned 12 vCPUs. The second VM is assigned 10 vCPUs. It gives 22 vCPUs in total. IBM MQ software is installed on both VMs.
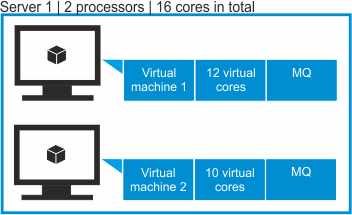
If a connection to the VM manager is not defined, BigFix Inventory does not have access to information about the number of sockets and physical cores on the server on which the VMs are deployed. It has access only to information about the number of vCPUs that each VM is assigned. The sum of vCPUs to which IBM MQ software has access is greater than the number of physical cores that are available on the server.
If a connection to the VM manager is not defined, the number of vCPUs to license is 22. If the connection is defined, 22 vCPUs are capped to 16 physical cores and thus the number of vCPUs to license is 16.