IAST configuration file
Configure a JSON file to override the default IAST settings, and
report only the vulnerabilities you want to know about.
Structure
The configuration file is user-config.json, and it can be deployed
either before the agent starts, or during runtime. Changes may take few seconds to
take effect. When a file is added, any previous version is disabled. If the file is
deleted, IAST returns to its default configuration.
{
"logging": {
"logLevel": "ERROR",
"stdoutLogLevel": "DEBUG",
"maxSizeLogFileMB": 100
},
"monitoredApps": [
"app1", "app2"
],
"asoc": {
"reportToAsoc": true,
"asocPollingIntervalInSec": 10
},
"memoryThreshold": 0.85,
"ignoredMethods": [
"DriverManager.getConnection"
],
"ignoredNonSecureCookies": [
"myCookieName"
],
"ignoredNonHttpOnlyCookies": [
"anotherCookieName"
],
"securityRules": {
"CheckCsrf": false,
"CheckServerHeader": false,
"CheckXPoweredBy": false,
"CheckXAspNetVersion": false
},
"safeHeaders": ["MySafeHeader", "MyOtherSafeHeader"],
"safeCookies": ["MySafeCookie", "MyOtherSafeCookie"],
"hidePasswords": true
"hooks": [
{
"targets": [
"com.ibm.myApp.common.MyEscapeUtils"
],
"methods": [
"myEscapeHtml"
],
"parameters": [
["java.lang.String"]
],
"rules": [
{
"type": " sanitizer",
"from": "return",
"vulnerability": "CrossSiteScripting.Reflected"
}
],
"requiresSuperTypes": false
}
]
} Deployment
Deploy the IAST agent through the ASoC RESP API or from a local file. In both cases you can update while IAST is actively monitoring, and the update will take effect within a few seconds.
REST API
- Send request
FileUpload. The response includesFileId.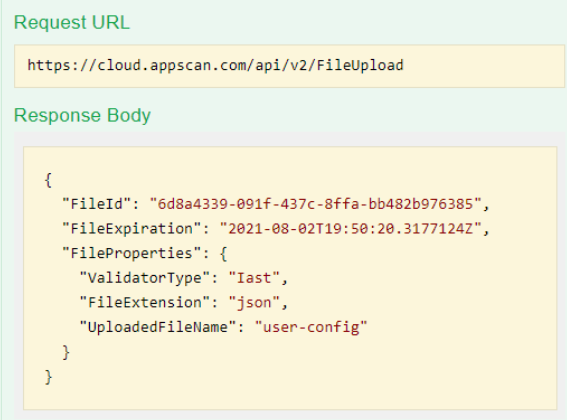
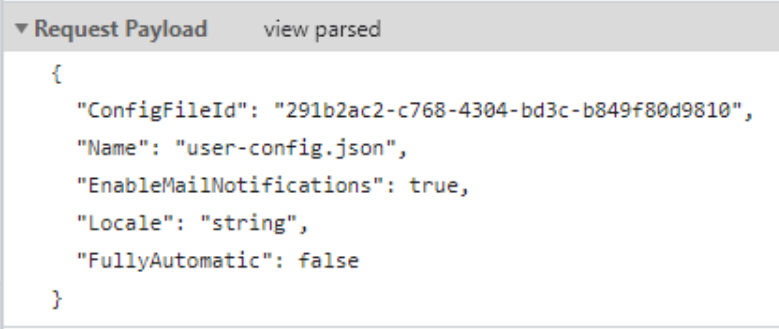
- Update your IAST agent with the
FileIdyou received.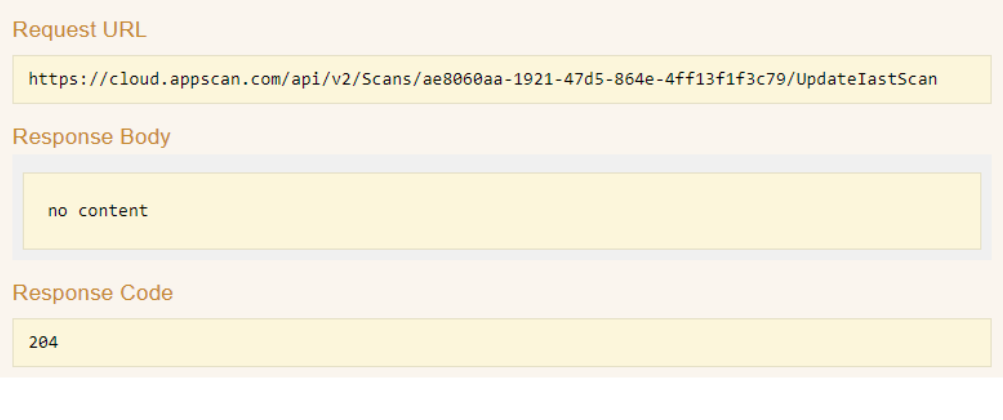
Local file
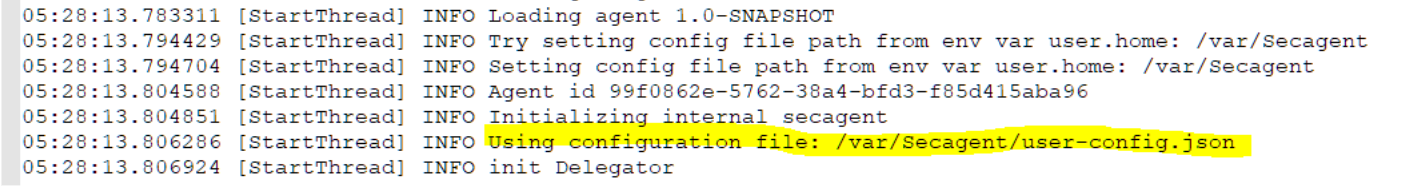
Deploy the configuration file by copying it to a directory on the server. The
deployment location usually is the server temp folder. last prints
the location to stout.
Options
Logging
| Field | Values | Description |
logLevel |
NONE, ERROR, WARNING, INFO, DEBUG, TRACE Default: DEBUG |
The logging level of IAST log file. Note: Setting the log level to TRACE can adversely affect IAST agent
performance. |
stdOutLogLevel |
ONE, ERROR, WARNING, INFO, DEBUG, TRACE Default: INFO |
The logging level of IAST events to stdout.Note: Setting the log level to any value other
than INFO adversely affects IAST agent performance. |
maxSizeLogFileMB |
Integer Default: 20 |
To avoid large files, when the IAST log file reaches a predefined maximum (in MB), it is zipped and the new logs are saved to a new file. Set the maximum file size with this field. |
Communication with ASoC
| Field | Values | Description |
reportToAsoc |
TRUE, FALSE Default: TRUE |
Enable or disable reporting to ASoC. |
asocPollingIntervalInSec |
Integer Default 10 |
Define how frequently (in seconds) IAST reports issues detected to
ASoC. Note: Reducing the
interval below 10s can create a large overhead on network
communications with ASoC. Increasing the
interval requires higher memory usage and may result in data loss if
the IAST agent is stopped before the latest data is sent to ASoC. |
General
| Field | Values | Description |
monitoredApp |
"monitoredApps": [ "app1", "app2"] will limit
monitoring to these apps only. |
Names the web applications running on the server that are to be
monitored by IAST; others will be ignored. If not defined, all applications on the server are monitored. The application name
generally is derived from the |
memoryThreshold |
Any value between 0.5 - 1.0 Default: 0.95 |
If the client's JVM memory usage runs above this threshold, IAST
automatically disables itself to prevent
OutOfMemoryError. When memory usage decreases below
the threshold, IAST automatically enables itself again. |
hidePasswords |
Boolean. Default: False | When set to True, passwords are not shown in the
user interface or report, but replaced with the string
**CONFIDENTIAL** |
Filtering
| Field | Values | Description |
ignoredMethods |
array of strings Default: None |
Filter out exploit issues (Cryptography.PoorEntrpy,
Cryptography.InsecureAlgorithm, and so on) based on namespace. Note: This exclude all issues from the
namespace. |
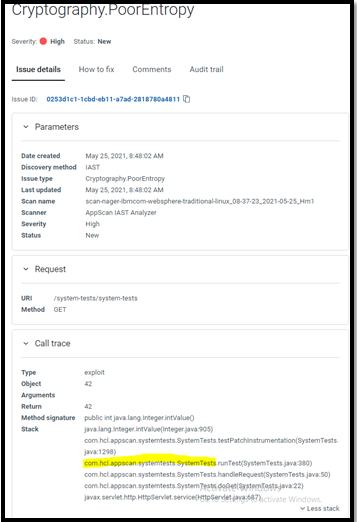
com.hcl.appscan.systemtests.SystemTests, add:
"ignoredMethods": ["com.hcl.appscan.systemtests.SystemTests"]| Field | Values | Description |
ignoredNonSecureCookies,
ignoredNonHttpOnlyCookies |
array of strings Default: None |
IAST reports when secure attribute is not set or http-only attribute of a cookie is set. To filter out a specific cookie, add the cookie name to the configuration file. |
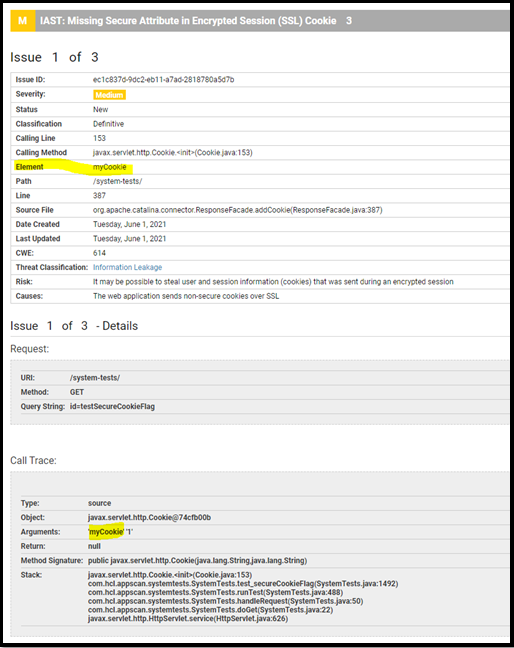 To filter out this
issue,
add:
To filter out this
issue,
add:"ignoredNonSecureCookies": ["myCookie"]Disable security rules
"securityRules": {
"CheckCsrf": false,
"CheckServerHeader": false,
"CheckXPoweredBy": false,
"CheckXAspNetVersion": false
}
} All security rules are enabled by default. Through the configuration file, you can disable some of the report types. Specify only the fields that you want to disable, all others will remain enabled.
“CheckCsrf” : false disables reporting for all issues of
this type.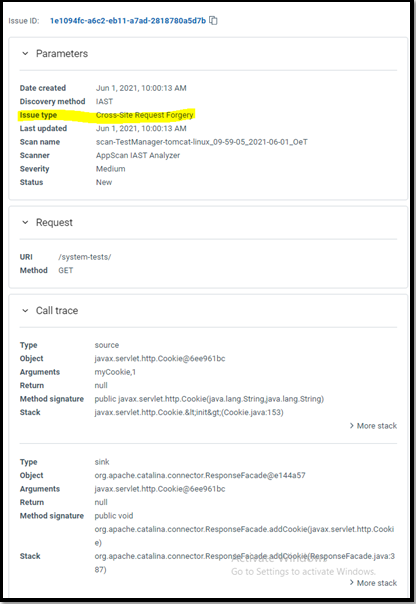
| Field | Values | Description |
safeHeaders, safeCookies |
array of strings Default: None |
Declare a header or a cookie value as safe by its name. This causes
IAST to stop tracking input from this header or cookie, so any
injection from this value will not be reported.
Tip: HTTP Header names are case
in-sensitive. |
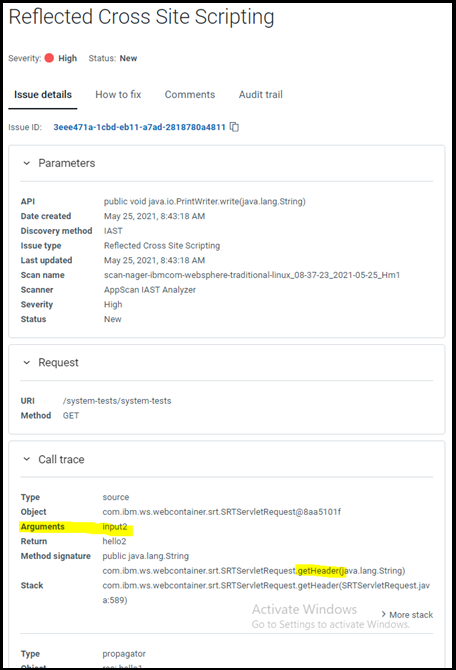
input2. To filter all issues caused by this input, add:
"safeHeaders": ["input2"]Hooks
Example 1: Sanitization for a specific vulnerability
myEscapeHtml in class
com.myApp.common.MyEscapeUtils as a sanitizer for cross-site
scripting, and the return value is cleaned. It still reports if the return value
ends up in an SQL sink. For
example."hooks": [
{
"targets": [
"com.myApp.common.MyEscapeUtils"
],
"methods": [
"myEscapeHtml"
],
"parameters": [
["java.lang.String"]
],
"rules": [
{
"type": "sanitizer",
"from": "return",
"vulnerability": "CrossSiteScripting.Reflected"
}
],
"requiresSuperTypes": false
}
] Example 2: Sanitization from all vulnerabilities
myEscapeAll in class
com.myApp.common.MyEscapeUtils as a sanitizer all vulnerability
types, and the return value is cleaned.
"hooks": [
{
"targets": [
"com.myApp.common.MyEscapeUtils"
],
"methods": [
"myEscapeAll"
],
"parameters": [
["java.lang.String"]
],
"rules": [
{
"type": " sanitizeAll",
"from": "return"
}
],
"requiresSuperTypes": false
}
]