Mobile access services
Mobile access services provide SafeLinx Clients with secure, virtual private network (VPN) access from external networks so that you can make enterprise applications and data available to your mobile workforce. Mobile access services support a wide range of wireless and dial-up networks.
SafeLinx Server to provide the communication interface for SafeLinx Clients. Mobile access services provide an optimized and secure IP tunnel for communication between the SafeLinx Server and SafeLinx Client software on a remote device. The SafeLinx Client can use a wireless or wireline connection to the mobile access services. This connection provides SafeLinx Clients with access to the private intranet of your company or to the internet.
- Data compression
- Data encryption
- Data optimization
- Authentication
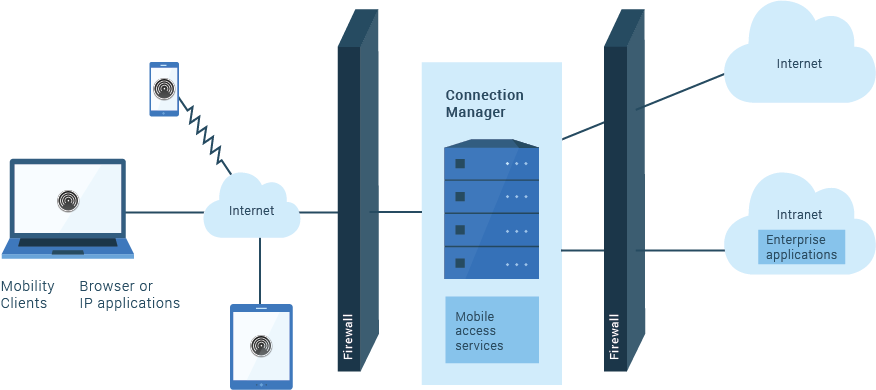
The SafeLinx Client software can connect to the SafeLinx Server from a wireless, dial-up, or LAN network. After a connection is established, the mobile access services enable the client to communicate with enterprise applications and with the Internet. In effect, the connection between the mobile access services and SafeLinx Clients is a proprietary virtual private network (VPN).
Mobile access services also support wireless applications that use non-IP packet-oriented connections.
- Groups, such as broadcast, filters, and packet mapping or NAT
- Connection profiles
- Network address translator (NAT)
- Packet mappings
- Filters
- Routing alias
- Mobile network interface (MNI)