Setting up an IBM i database in a cluster | HCL Digital Experience
To communicate with a database, servers that run IBM i can use either of two JDBC drivers: the IBM Toolbox for Java JDBC driver or the IBM Developer Kit for Java JDBC driver (also referred to as the native JDBC driver). Which JDBC driver you must use depends on how you are setting up your clustered environment.
The JDBC driver is specified by the
db2_iseries.DbDriver property
in the wkplc_dbtype.properties file,
which is in thewp_profile_root/ConfigEngine/properties directory. You can specify the
value by editing the file manually or by selecting the appropriate
value by using the Configuration Wizard.- Native JDBC driver:
com.ibm.db2.jdbc.app.DB2Driver - IBM Toolbox for Java JDBC driver:
com.ibm.as400.access.AS400JDBCDriver
Scaling topology considerations
Vertical
and horizontal scaling topologies in an IBM® i environment
require different JDBC driver configurations, according to how you
deploy your database.
| Scaling topology | JDBC driver considerations |
|---|---|
| Vertical scaling | When you sett up a vertical cluster, you can install the
database locally on the same machine as your portal or remotely on
a separate machine. Use the appropriate JDBC driver, depending on
where the database is installed.
|
| Horizontal scaling | When you set up a horizontal cluster, you must use the IBM Toolbox for Java JDBC driver. The typical configuration is to use a remote database for primary and secondary nodes in the cluster. If you choose, you can use a local database for the primary node and configure the secondary nodes to use that database, just as you would any other remote database. However, regardless of whether you choose to include a local database in your environment, you must use the IBM Toolbox for Java JDBC driver with your horizontal cluster. |
Using a local database in an IBM® i horizontal cluster
Although
the instructions for setting up a horizontal cluster describe how
to use a remote database for both primary and secondary nodes, you
can choose to configure your IBM® i horizontal cluster
to use a local database for the primary node instead. In this example,
a database and Web Server are locally installed on the system (System
1) where IBM® WebSphere® Portal and IBM WebSphere Application Server
are installed. System 1 is the primary node. System 2 is the secondary
node. 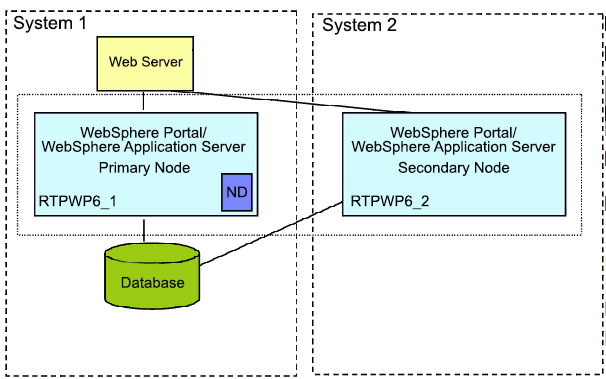

Note: Although it is possible to use a local
database on a secondary node instead of the primary node, this configuration
is not tested and is not documented here.
Important: Even
though you are using a local database for the primary node in this
scenario, all database connections are configured as if the database
were remote. Specifically, you must use the IBM Toolbox for Java JDBC
driver (com.ibm.as400.access.AS400JDBCDriver) when you configure the
database for both primary and secondary nodes.
To use
a local database with your primary node, do the database configuration,
with the following variations when you update the properties files
in thewp_profile_root/ConfigEngine directory.
- wkplc_dbtype.properties
-
- Specify the JDBC driver in the
db2_iseries.DbDriverproperty. For example:db2_iseries.DbDriver=com.ibm.as400.access.AS400JDBCDriver - Specify the database location as remote in the
db2_iseries.DbDriverTypeproperty. For example:db2_iseries.DbDriverType=4
- Specify the JDBC driver in the
- wkplc_dbdomain.properties
-
- Specify the primary node's host name for the
domain.DbNameproperties. For example: release.DbName=primary_host_name/wpsdb - Specify the primary node's host name in the
domain.DbUrlproperties. For example: release.DbUrl=jdbc:as400:primary_host_name/wpsdb
- Specify the primary node's host name for the
Note: If you use the configuration wizard for database
transfer, update the values in the wizard panels rather than in the
properties files.
Complete all other configuration as described. When you configure secondary nodes in this scenario, do your database configuration as you would for any remote database, by using the primary node's host name for the database transfer.