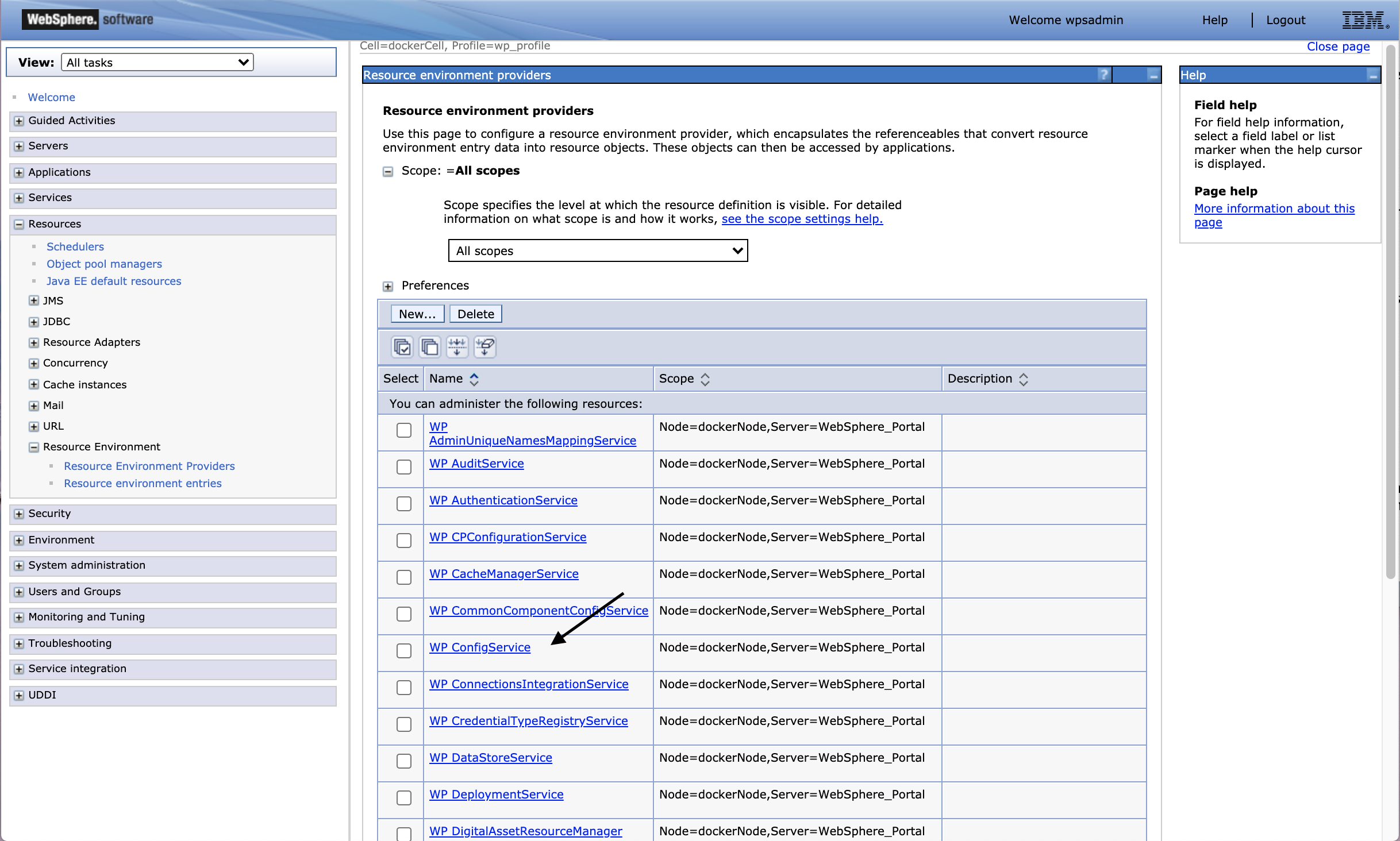
WP_ConfigService Resource Environment Parameters (REP) for Content Security Policy configuration | HCL Digital Experience
The following WebSphere Application Server (WAS) resource environment parameters are used to configure CSP.
- csp-enabled
- Set to
‘true’if CSP is enabled. - csp-report-enabled
- Set to
‘true’if CSP reporting is enabled. - csp-header
- Set to the desired CSP allowlist
Default: default-src 'self'; script-src 'self' 'nonce-default'; img-src 'self' data:; style-src 'self' 'nonce-default’;. - csp-header-report
- Set to the desired CSP report allowlist
Default: default-src 'self'; script-src 'self' 'nonce-default'; img-src 'self' data:; style-src 'self' 'nonce-default';
These parameters are included under the WP_ConfigService resource
environment provider custom properties.
csp-replace-string parameter
In addition, the csp-replace-string plus a number (for example,
csp-replace-string.1) configures find-and-replace strings used
in the CSP filter. This parameter is designed to allow users to implement filtering
to correct their site-specific CSP issues.
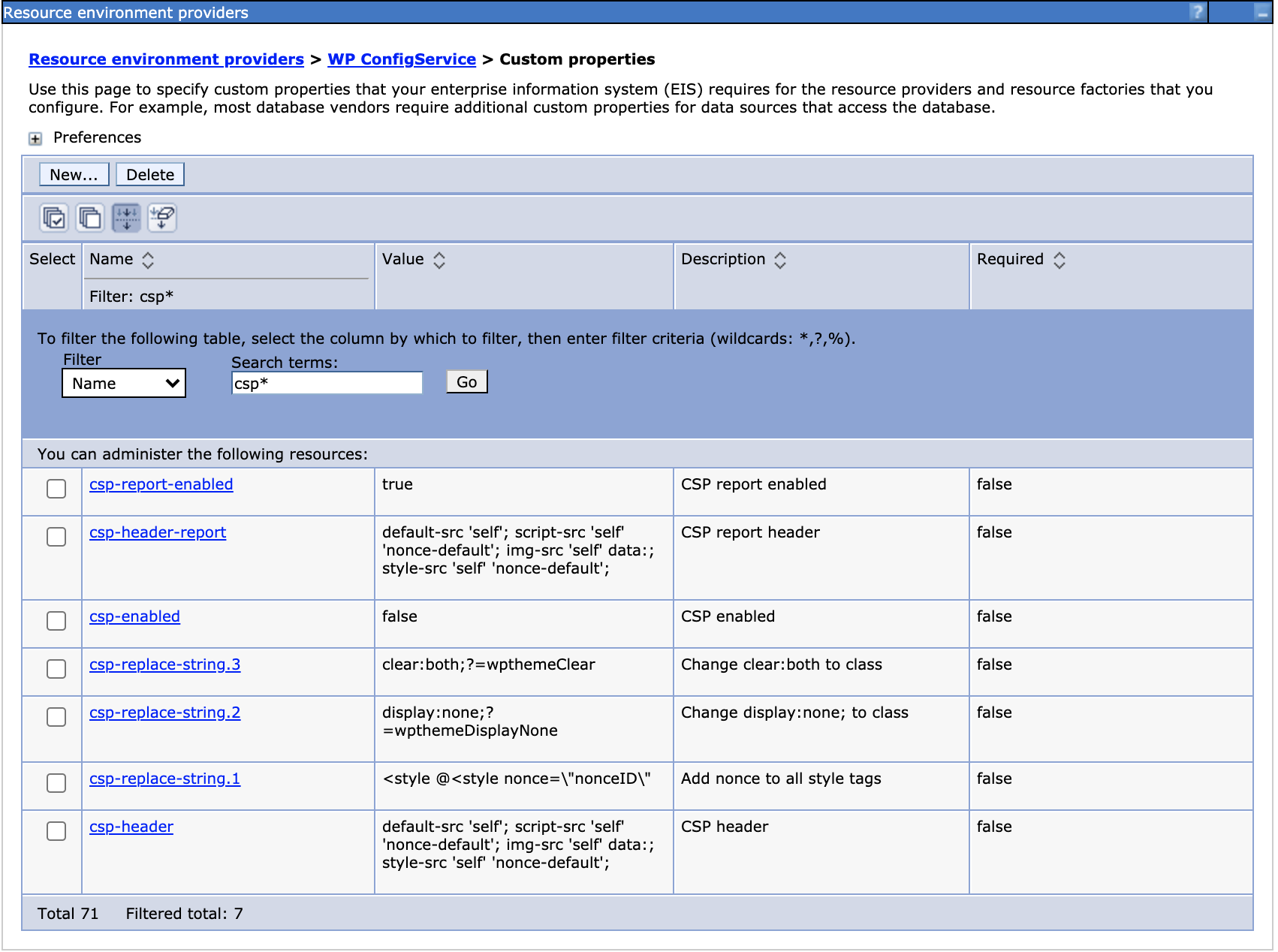
Separators '@' and '=’
The following separators are used with the csp-replace-string
parameter:
- Literal string replacements
The separator
'@'does a literal find/replace in the markup.For example, the out-of-the-boxcsp-replace-string.1is:<style @<style nonce=\"nonceID\"This parameter replaces the string referencing the style element preceding the
'@'with the string following the'@'(a string for string replacement). Please note that the quotations in the string are being escaped using the \ character and that "nonceID" is an internal keyword that signals the filter to call the nonce service for a nonce to go in the place of "nonceID".Customers can use this literal find/replace to append a nonce to any inline script that they choose to permit in custom code. However, as previously stated, this is considered risky. An option for developers is to use a "shared secret" placed on script tags that contains a nonce value. This "shared secret" can be shared with the Portal admin creating the resource environment parameters used by the filter.
For example,<script secret!abc @<script nonce=\"nonceID\"specifies that a nonce value is placed on this script tag.
- Style replacementsNote: Use the search and replace described here only for style replacements.
The separator
'='searches the markup for the regex value preceding the'='and replaces it on the element with the CSS class following the'='.Out-of-the-box, DX filters CSS inline styles of"display:none"and"clear:both"and adds the necessary classes to the DOM element. The format of the parameter is:regex find string = replacement classFor example:
replaces eitherdisplay:none;?=wpthemeDisplayNonestyle="display:none"orstyle="display:none;"withclass="wpthemeDisplayNone".In addition, the replacement considers whether or not a class attribute already exists in the element. For example:
is changed to:<div style="display:none"></div><div class="wpthemeDisplayNone"></div>However, this element
is changed to:<div class = "abc" style="display:none"></div><div class="abc wpthemeDisplayNone"></div>