Integrating WebSphere Commerce with third-party search engines
Integrating WebSphere Commerce Search with third-party search engines other than Apache Solr can be accomplished by modifying default interfaces and performing other customizations to meet your business requirements. However, it is important to note that this process is an advanced task, as WebSphere Commerce Search is a core runtime component in WebSphere Commerce. Many features are tightly integrated with the search component. Therefore, replacing WebSphere Commerce Search with a third-party search engine is an in-depth customization.
That is, there are many existing (and future) features that are tightly integrated with the search component. Therefore, replacing WebSphere Commerce Search with a third-party search engine can cause malfunctions, requiring in-depth customization to recover and replicate WebSphere Commerce search functions.
- All Management Center functions related to WebSphere Commerce Search, such as search term associations, search rules, search rule-based e-Marketing Spot product recommendation, search statistics, and search facets.
- Rule-based catalog entitlement (catalog filtering)
- Commerce Composer
- Price rules that use catalog filters
- Configurator
- Workspace preview
- Lifecycle management on the search index
- Caching and invalidation
Procedure
-
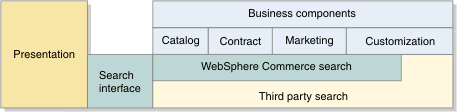
The following diagram highlights the integration strategy with an extra third-party search
service provider:
Where:
- Across the top is a layer of business components, such as Catalog, Contract, and Marketing. Each of these components is responsible for contributing a portion of the search expression and later combined by run time to form a master execution instruction for the search engine.
- WebSphere Commerce Search is the search implementation that is provided by default. Its advantage is that it engages tighter integration with other existing WebSphere Commerce business components and optimizes the processing logic to gain better overall performance throughput at run time.
- A search interface is provided for search integration. Using this search interface, it is possible to reuse similar XPath expressions against a different third-party search service provider, and display the search result directly on the presentation layer.
-
Custom logic can be implemented:
- Following the recommended programming pattern with WebSphere Commerce Search, or
- Code directly against other search service providers and aggregate the search result at the storefront user interface.
Note:- Both of these approaches can use the same search interface to maintain consistency in the user interface.
- The Management Center cannot be used to manage other custom third-party search implementations.
-
The following key considerations must be understood when you use other third-party search
engines: