Modifying global scan options
You can control the behavior of the global scan through the Configure Filesystems Scan Options task.
UNIX content includes a global scan script that is used to do a full system scan. The results of this scan are used in a number of scripts. This script eliminates the need to run a full system scan multiple times when you are evaluating a set of checks on a single system. This feature allows Endpoint Manager to be more efficient and causes less impact on the system during a configuration scan.
The global scan script runs by default when you are using the Endpoint Manager Deploy and Run Security Checklist task. It is used by the Master Run script with the use of the –g option. The behavior of the global scan script can be controlled through the Configure Filesystems Scan Options task.
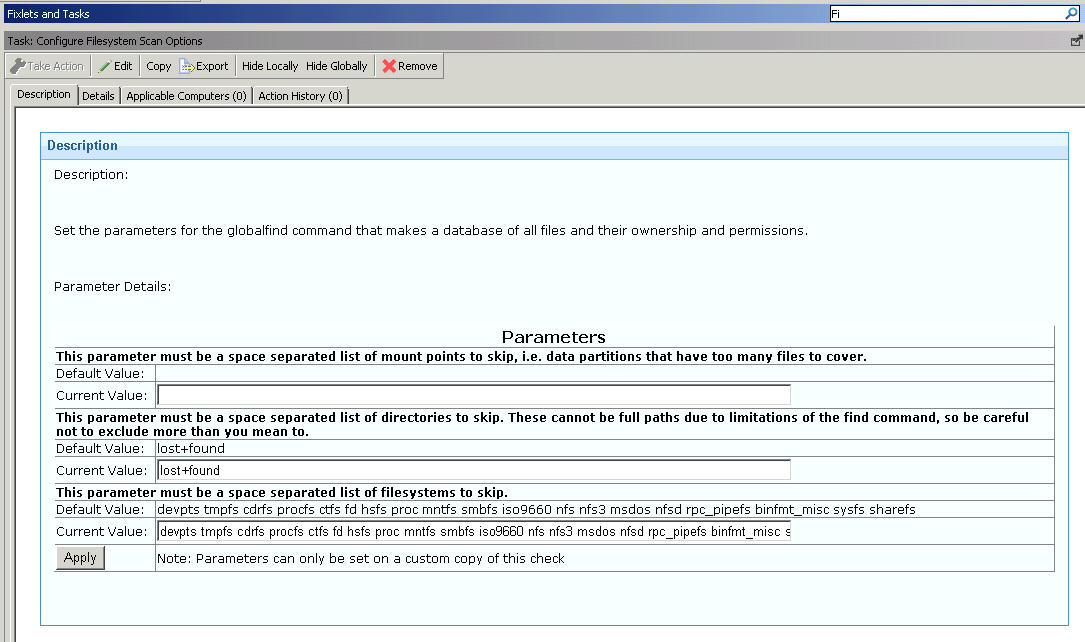
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| EXCLUDEFS | A list of specific file systems to exclude from scanning. This list must be a space-separated list of all the file system types to exclude from the search. By default, the global find script excludes the following file system types from its search:
|
| EXCLUDEMOUNTS | A list of specific mount points to exclude from scanning. This parameter must
be defined as a space-separated list of all the file system mounts to
exclude from the search. This prevents the shared file system from being
scanned from multiple systems. For example, if several systems mount a shared directory on a Storage Area Network named /san, you might want to exclude them with a parameter such as: EXCLUDEMOUNTS="/san" By default, this parameter is not used and is represented as an empty value. |
| EXCLUDEDIRS | List of directories to exclude from scanning. Any directory names specified in EXCLUDEDIRS are omitted from the directory listing. By default, this parameter excludes the lost+found directory. |