Nginx load balancer algorithms
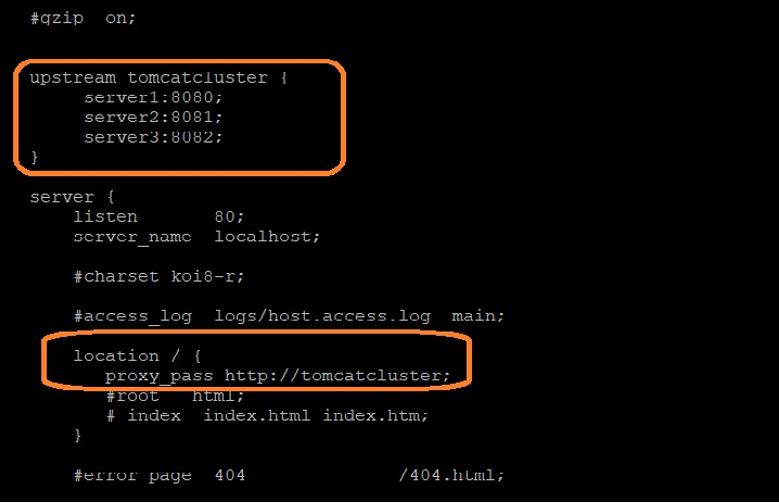
- Round-robin: Requests to the application servers are distributed in a round-robin
fashion. The following is the sample configuration (<NGINX_HOME>/conf/
nginx.conf) with round robin fashion.
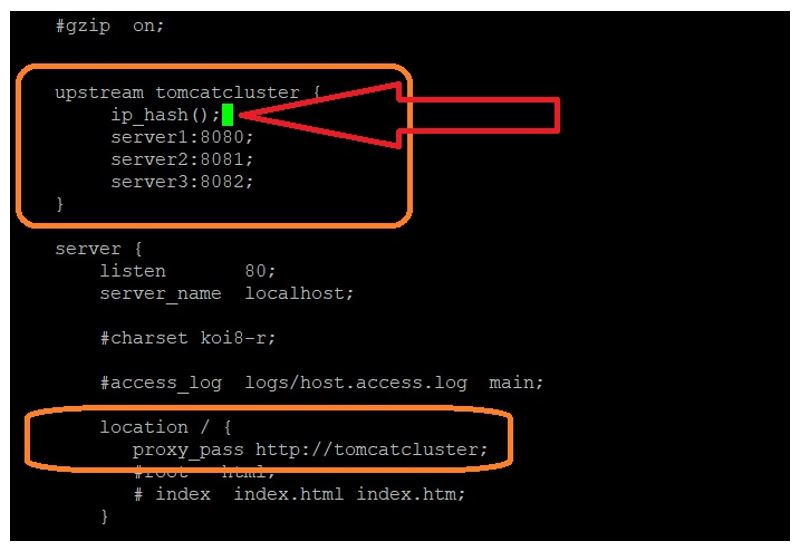
- Ip_hash: With ip-hash, the client’s IP address is used as a hashing key to determine
the server to be selected in a server group for the client’s requests.
This method ensures that the requests from the same client are always directed to the same server except when this server is unavailable.
The following is the sample configuration (<NGINX_HOME>/conf/nginx.conf) with round robin fashion. - Least_conn: With the least-connected load balancing, nginx tries not to overload a busy application server with excessive requests, distributing the new requests to a less busy server instead.
- Weight Distribution (weigth n): With this configuration, every five new requests are
distributed across the application instances as the following:
- Three requests are directed to srv1.
- One request goes to srv2.
- Another one goes to srv3.
Upstream tomcatcluster
{ Server server1:8080 weight 3; Server server2:8081; Server server4:8082; } - Max Fails configuration: Max fails refers to the maximum number of failed attempts to connect to a server must occur before it is considered inactive. Fall_timeout specifies the length of that the server is considered inoperative. Once the time expires, new attempts to reach the server will start up again. The default timeout value is 10 seconds.
- For example:
Upstream tomcatcluster
{ Server server1:8080 max_fails=3 fail_timeout=15s; Server server2:8081; Server server4:8082; }