Multiple connection types
A single instance of the database server can provide more than one type of connection.
The following figure illustrates a configuration with more than one type of connection. The database server is on host river. Client A connects to the database server with a shared-memory connection because shared memory is fast. Client B must use a network connection because the client and server are on different computers.
- Add DBSERVERNAME and DBSERVERALIASES entries in the onconfig file.
- Add an sqlhosts entry for each database server/connection type pair.
DBSERVERNAME river_net
DBSERVERALIASES river_shm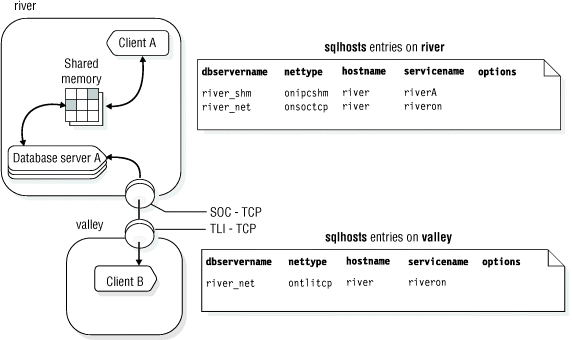
CONNECT TO '@river_shm'In the sqlhosts file, the nettype associated with the name river_shm specifies a shared-memory connection, so this connection is a shared-memory connection.
CONNECT TO '@river_net'In the sqlhosts file, the nettype value associated with river_net specifies a network (TCP/IP) connection, so Client B uses a network connection.