Audit process
When you turn on auditing, the database server generates audit records for every event that the auditing instructions specify.
The database server stores the audit records in an audit file. The collection of audit records makes up the audit trail. (The audit trail might consist of more than one audit file.)
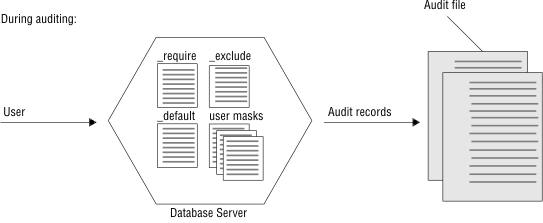
An audit administrator must specify and maintain the audit configuration, which includes the following information:
- The audit mode
- How the database server behaves if it encounters an error when writing audit records to the audit trail
- For UNIX™, the directory in which the audit trail is located
- For UNIX, the maximum size of an audit file before the database server automatically starts another audit file
These topics are explained in Audit configuration.
The database server generates audit records and writes them to the audit file or to an event log regardless of whether the client user that performs the audited action is local or remote. The database server includes both the user login and database server name in every audit record to help pinpoint a specific initiator and action.