When code-set conversion is performed
An application must use code-set conversion only if the two code sets (client and server-processing locale, or server-processing locale and server) are different.
- Different operating systems might encode the same characters in different ways.
For example, the code for the character ac (a-circumflex) in Windows™ Code Page 1252 is hexadecimal 0xE2. In HCL Coded Character Set Identifier (CCSID) 437 (a common HCL UNIX™ code set), the code is hexadecimal 0x83. If the code for ac on the client is sent unchanged to the HCL UNIX computer, it prints as the Greek character g (gamma). This action occurs because the code for g is hexadecimal 0xE2 on the HCL UNIX computer.
- One language can have several code sets. Each might represent
a subset of the language.
For example, the code sets ccdc and big5 are both internal representations of a subset of the Chinese language. These subsets, however, include different numbers of Chinese characters.
- If the client locale and database locale specify different code sets, the client application performs code-set conversion so that the server computer is not loaded with this type of processing. For more information, see Client application code-set conversion.
- If the server locale and server-processing locale specify different code sets, the database server performs code-set conversion when it writes to and reads from operating-system files such as log files. For more information, see Database server code-set conversion.
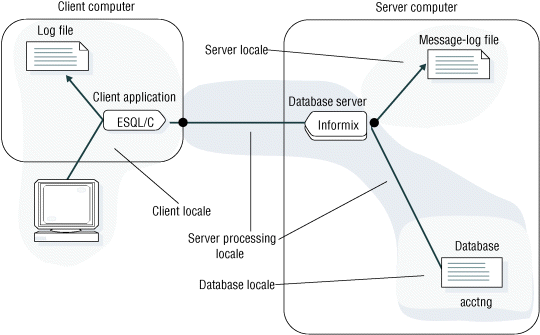
In the example connection that the previous figure shows, the client application performs code-set conversion on the data that it sends to and receives from the database server if the client and database code sets are convertible. The HCL OneDB database server also performs code-set conversion when it writes to a message-log file if the code sets of the server locale and server-processing locale are convertible.