Update-Anywhere Replication System
In update-anywhere replication, changes made on any participating database server are replicated to all other participating database servers. This capability allows users to function autonomously even when other systems or networks in the replication system are not available.
The following figure illustrates an update-anywhere replication system where the service centers in Washington, New York, and Los Angeles each replicate changes to the other two servers.
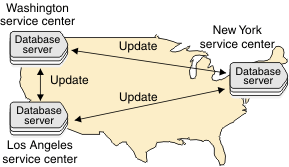
Because each service center can update a copy of the data, conflicts can occur when the data is replicated to the other sites. To resolve update conflicts, Enterprise Replication uses conflict resolution.
- Administration
Update-anywhere replication systems allow peer-to-peer updates, and therefore require conflict-resolution. Update-anywhere replication systems require more administration than primary-target replication systems.
- Information consistency
Some risk is associated with delivering consistent information in an update-anywhere replication system. You determine the amount of risk based on the type of conflict-resolution rules and routines you choose for resolving conflicts. You can configure an update-anywhere replication system where no data is ever lost; however, you might find that other factors (for example, performance) outweigh your need for a fail-safe mechanism to deliver consistent information.
- Capacity Planning
All replication systems require you to plan for capacity changes and prepare the data for replication. If you choose a time-based conflict resolution rule, you need to provide space for delete tables and add shadow columns to replicated tables.
- High Availability
If any of your database servers are critical, consider using high-availability clusters to provide backup servers.