Let's Encrypt certificate request flow for HTTP-01 challenges
The following diagram illustrates the components and steps involved in a certificate request to the Let's Encrypt® CA when HTTP-01 challenges are used.
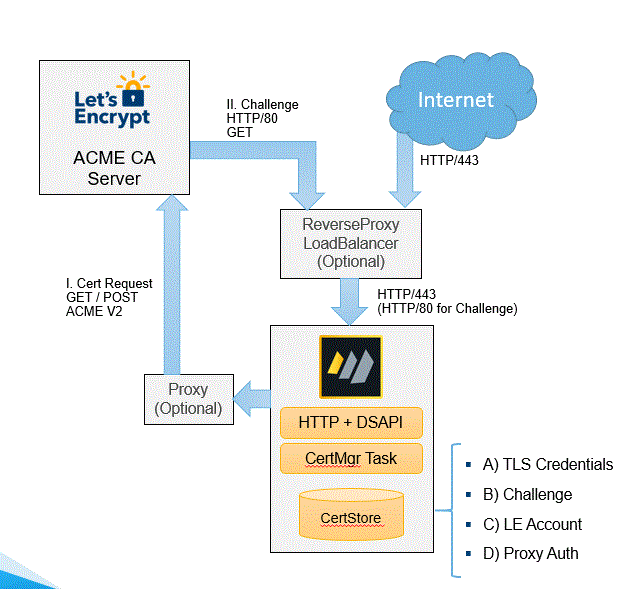
Components
Diagram key:
(A) Formerly stored in kyr file
(B) Challenge needed to verify request
(C) ACME account credentials used to authenticate with ACME-based CA such as the Let's Encrypt CA
(D) Proxy account needed for outgoing communication if needed
Flow
- CertMgr creates account (C) with ACME CA server
- CertMgr creates key pair and writes it to CertStore (A)
- CertMgr creates CSR and sends it to ACME CA server
- CertMgr saves received challenge (B) in CertStore
- ACME CA server requests challenge on port 80 to verify domain ownership
- Domino HTTP replies with challenge (B) from CertStore
- CertMgr receives certificate chain and writes it to CertStore (A)
- HTTP (and INET tasks) read certificates and keys from CertStore (A)
Notes
- certstore.nsf should be replicated to all servers that access it. Access to the Let's Encrypt CA is always over HTTP(S) not "local or NRPC".
- Domino HTTP and CertMgr task can run on separate Domino servers that share the CertStore.
- Proxy communication uses Proxy user (D)